297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
문제
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
예제 입출력
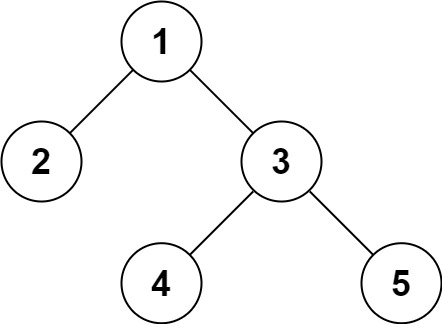
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
You can read the full description here.
풀이 1
접근법: 직렬화
- BFS로 풀이합니다.
- 큐에 루트를 넣습니다.
- 큐에서 큐 길이만큼 빼서 값은 temp에 모아주고, None이 아니라면 다시 큐에 모아줍니다.
- temp가 모두 None이 아니라면 result 배열에 기록합니다.
- temp 마지막이 연속적으로 None인 경우 이를 제거합니다.
접근법: 역직렬화
- 마찬가지로 BFS로 풀이합니다.
- 루트를 큐에 넣습니다.
- 루트를 제외한 노드를 뒤집어서 children으로 사용합니다.(pop을 이용합니다.)
- 현재 children이 None이라면 pop만 수행하고, 아니라면 새 노드를 만들어 연결하고 큐에 넣습니다.
구현 코드
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
import collections
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
if not root:
return '[]'
res = [root.val]
q = deque()
q.append(root)
while q:
temp = []
for _ in range(len(q)):
cur = q.popleft()
if cur.left:
q.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
q.append(cur.right)
temp.extend([cur.left.val if cur.left else None, cur.right.val if cur.right else None])
if not set(temp) == {None}:
res.extend(temp)
while res[-1] == None:
res.pop()
return '['+','.join(list(map(str,res)))+']'
def deserialize(self, data: str) -> TreeNode:
nodes = list(map(lambda x: int(x) if x.lstrip('-').isnumeric() else None, data[1:-1].split(',')))
if nodes == [None]:
return None
if len(nodes) == 1:
return TreeNode(nodes[0])
children = nodes[::-1]
root = TreeNode(children.pop())
q = deque()
q.append(root)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
if children:
if children[-1] == None:
children.pop()
else:
left = TreeNode(children.pop())
cur.left = left
q.append(left)
if children:
if children[-1] == None:
children.pop()
else:
right = TreeNode(children.pop())
cur.right = right
q.append(right)
return root
책에 있는 풀이
원본 코드는 여기에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
풀이 2
접근법: 직렬화
- BFS로 풀이합니다.
- 역직렬화에서 편한 계산을 위해 1-indexed로 배열을 구성합니다. 0번 인덱스에는 None을 의미하는 #을 넣습니다.
- 큐에서 뺀 노드가 None이면 # 을 결과 배열에 추가합니다.
- None이 아니면 값을 추가하고 다시 큐에 넣어줍니다.
접근법: 역직렬화
- BFS로 풀이합니다.
- 큐에 들어가는 노드와 별개로 자식을 가리키는 인덱스를 설정합니다.
- 자식 인덱스가 None(#)이 아닌경우 다시 큐에 넣어줍니다.
구현 코드
import collections
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Codec:
# 직렬화
def serialize(self, root: TreeNode) -> str:
queue = collections.deque([root])
result = ['#']
# 트리 BFS 직렬화
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node:
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
result.append(str(node.val))
else:
result.append('#')
return ' '.join(result)
# 역직렬화
def deserialize(self, data: str) -> TreeNode:
# 예외 처리
if data == '# #':
return None
nodes = data.split()
root = TreeNode(int(nodes[1]))
queue = collections.deque([root])
index = 2
# 빠른 런너처럼 자식 노드 결과 먼저 확인 후 큐 삽입
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if nodes[index] is not '#':
node.left = TreeNode(int(nodes[index]))
queue.append(node.left)
index += 1
if nodes[index] is not '#':
node.right = TreeNode(int(nodes[index]))
queue.append(node.right)
index += 1
return root